Ultrasound in Medicine: Applications and Risks
Ultrasound in Medicine: Applications and Risks The use of ultrasound in medicine has developed into an indispensable tool for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in recent decades. Ultrasonic waves are sound waves with a frequency above the range perceptible by the human ear, namely over 20,000 hertz (Hz). These high-frequency sound waves can penetrate through tissue and fluids in the body and provide important information about the structure and function of organs, tissues and vessels. Applications of Ultrasound in Medicine Ultrasound is now used in numerous medical areas. Here are some of the most common applications: Diagnostics Sonography, i.e. imaging using...
Ultrasound in Medicine: Applications and Risks
Ultrasound in Medicine: Applications and Risks
The use of ultrasound in medicine has developed into an indispensable tool for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in recent decades. Ultrasonic waves are sound waves with a frequency above the range perceptible by the human ear, namely over 20,000 hertz (Hz). These high-frequency sound waves can penetrate through tissue and fluids in the body and provide important information about the structure and function of organs, tissues and vessels.
Applications of ultrasound in medicine
Ultrasound is now used in numerous medical areas. Here are some of the most common uses:
Diagnostics
Sonography, i.e. imaging using ultrasound, is a common method for diagnosing various diseases or injuries. By recording real-time images, a doctor can visualize organs such as the heart, liver, kidneys or uterus and examine them for any irregularities. These images can be used, for example, to detect tumors or identify fluid accumulations.
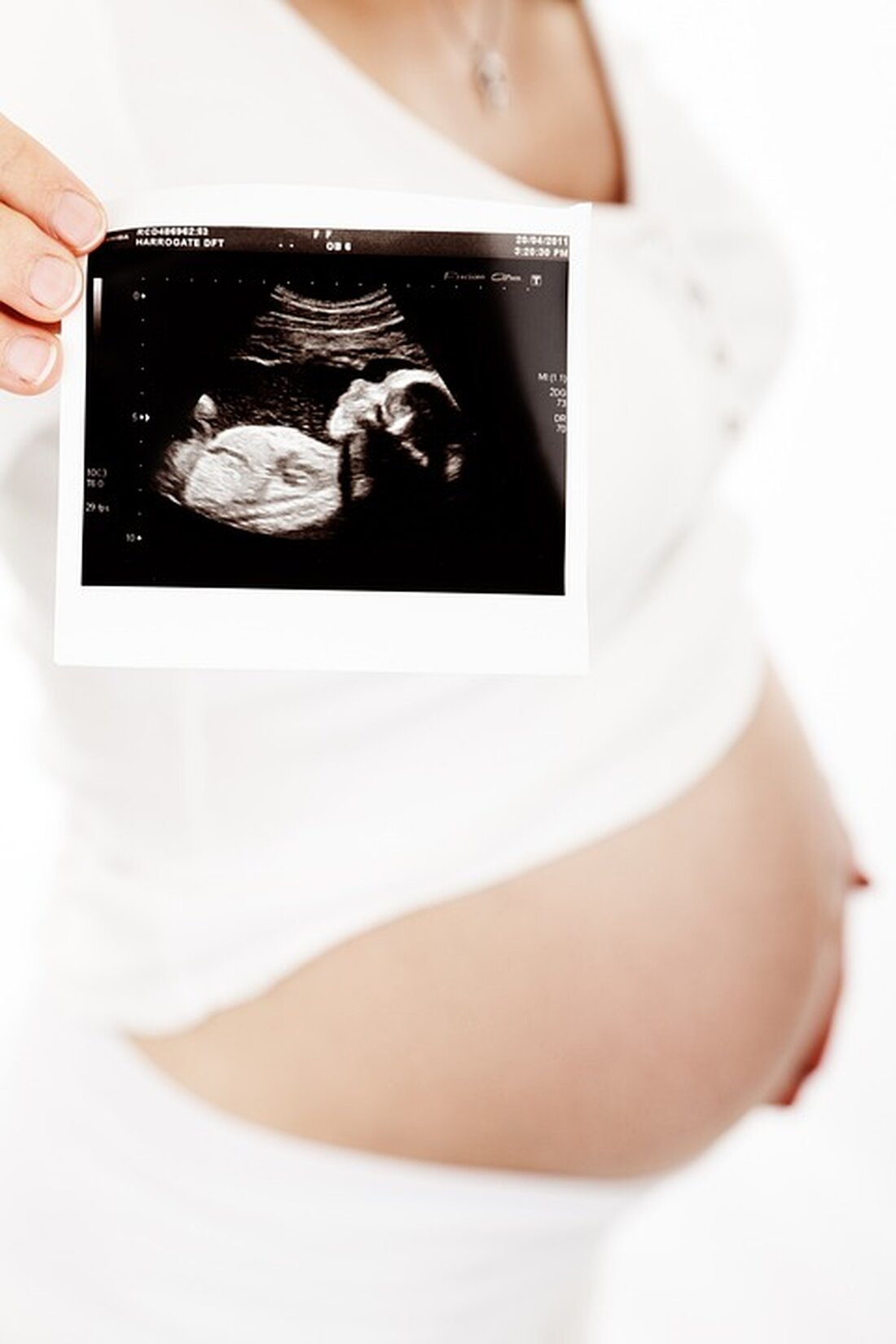
Prenatal care
One of the most well-known uses of ultrasound is prenatal imaging during pregnancy. The so-called “ultrasound pregnancy care” allows doctors to monitor the growth of the fetus and detect possible abnormalities at an early stage. Ultrasound images also offer expectant parents the opportunity to see their unborn child in 2D, 3D or even 4D images.
Vascular diagnostics
Doppler ultrasound is a special form of sonographic examination that measures the speed and direction of blood flow in the blood vessels. This procedure allows doctors to detect circulatory disorders, such as narrowing (stenosis) or blockages of arteries. Doppler ultrasound plays an important role in detecting vascular diseases such as atherosclerosis or thrombosis.
Interventional procedures
Ultrasound can also be used during minimally invasive surgical procedures to provide the surgeon with real-time images and help them navigate the body. Examples of such interventional ultrasound procedures include the biopsy of tumors (tissue removal for further analysis), the puncture of fluid collections for drainage, and ultrasound-controlled injections of medication into specific locations in the body.
Risks associated with ultrasound diagnosis
Although ultrasound scans are relatively safe and have no known harmful effects on the human body, there are still certain precautions to be taken:
Not pointless frequent applications
Although ultrasound scans are generally safe, it is recommended that they not be performed without a good reason. There is no scientifically based evidence for routine sonography without medical necessity. Physicians should responsibly decide on the use of ultrasound based on the patient's individual medical history and symptoms.
Safety guidelines during pregnancy
The use of ultrasound should be carefully considered during pregnancy. Although studies have so far shown no harmful effects on embryos or fetuses, it is recommended to avoid unnecessary sonographic examinations during pregnancy and only perform them if medically justified.
FAQs
Ask:Is an ultrasound diagnosis painful?
Answer:No, an ultrasound diagnosis is usually painless. The examining doctor applies a gel to the skin and passes a transducer over it to produce images. This procedure is non-invasive and usually comfortable for the patient.
Ask:How long does a typical ultrasound diagnosis take?
Answer:The duration of an ultrasound diagnosis depends on various factors. In general, a basic examination takes about 15-30 minutes. The time may vary depending on the area to be examined, the aim of the examination and the level of difficulty.
Ask:Are there any contraindications to ultrasound examinations?
Answer:Yes, there are certain situations in which ultrasound should not be used or should only be used with caution. These include open wounds in the area to be examined or the use of ultrasound-sensitive implants such as pacemakers or high-risk pregnancies.
conclusion
Ultrasound has established itself as a versatile tool in medicine and is used for various purposes including diagnostics, prenatal care, vascular diagnostics and interventional procedures. The use of ultrasound is safe and has no known harmful effects on the body. However, it is important to use this technology responsibly and only use it when medically necessary.
Sources:
– https://www.radiologyinfo.org/
– https://www.mayoclinic.org/

 Suche
Suche
 Mein Konto
Mein Konto
