Claudication
Claudication
overview
Claudication
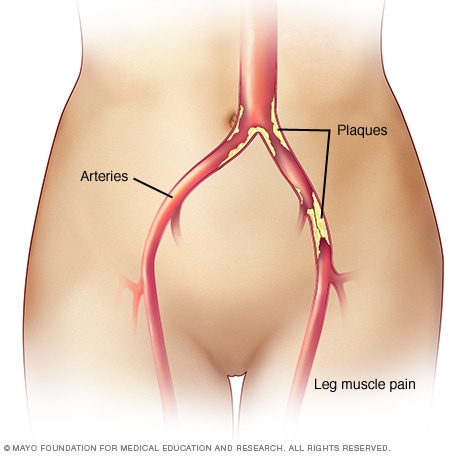
Claudication
Claudication is pain in the legs or arms that occurs when walking or using the arms. The pain is caused by insufficient blood flow to the legs or arms. Claudication is usually a symptom of peripheral artery disease, in which the arteries that supply blood to the arms or legs, usually the legs, are narrowed. The narrowing is usually due to a buildup of fatty deposits (plaques) on the artery walls.
Claudication is pain caused by insufficient blood flow to the muscles during exercise. Most often, this pain in the legs occurs after walking at a certain pace and for a certain time - depending on the severity of the condition.
The condition is also called intermittent claudication because the pain is usually not constant. It starts during exercise and ends with rest. However, if claudication worsens, the pain may occur at rest.
Claudication is technically a symptom of a disease, usually peripheral artery disease, a narrowing of the arteries in the limbs that restricts blood flow.
Treatments focus on reducing the risk of vascular disease, reducing pain, increasing mobility and preventing tissue damage.
Symptoms
Claudication refers to muscle pain due to lack of oxygen, triggered by activity and relieved by rest. Symptoms include:
- Schmerzen, Schmerzen, Unbehagen oder Ermüdung in den Muskeln bei jeder Verwendung dieser Muskeln
- Schmerzen in Waden, Oberschenkeln, Gesäß, Hüften oder Füßen
- Seltener Schmerzen in Schultern, Bizeps und Unterarmen
- Schmerzen, die bald nach dem Ausruhen besser werden
The pain may become worse over time. You may even start to have pain at rest.
Signs or symptoms of peripheral artery disease, usually in more advanced stages, include:
- Kühle Haut
- Starke, anhaltende Schmerzen, die zu Taubheit führen
- Hautverfärbung
- Wunden, die nicht heilen
When to go to the doctor?
Talk to your doctor if you experience pain in your legs or arms while exercising. Claudication can lead to a cycle that leads to worsening cardiovascular health. Pain can make exercise unbearable, and a lack of exercise leads to poorer health.
Peripheral arterial disease is a sign of poor cardiovascular health and an increased risk of heart attack and stroke.
Other medical conditions that affect the blood, nerves, and bones can contribute to leg and arm pain during exercise. It is important that a complete examination and appropriate testing be performed to diagnose possible causes of pain.
Causes
Development of atherosclerosis
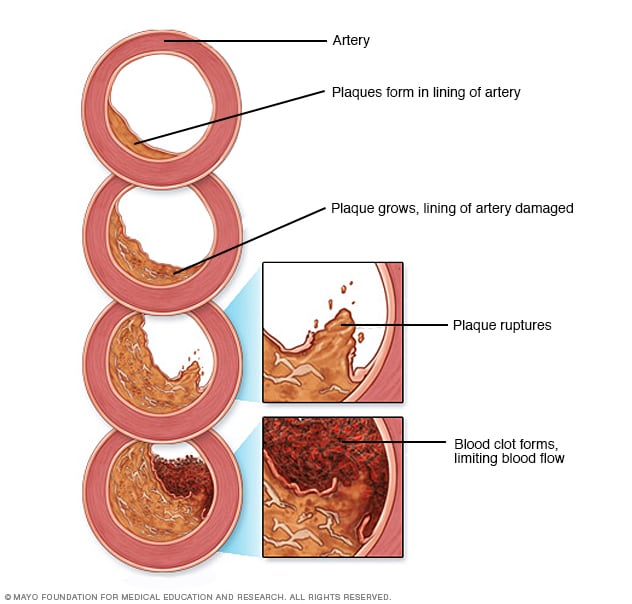
Development of atherosclerosis
When there are too many cholesterol particles in the blood, cholesterol can build up on the artery walls. Eventually, deposits called plaques can form. The deposits can narrow – or block – the arteries. If the plaques rupture, a blood clot can form.
Claudication is most often a symptom of peripheral arterial disease. The peripheral arteries are the large vessels that supply blood to the legs and arms.
Peripheral arterial disease is damage to an artery that restricts blood flow in an arm or leg (limb). When resting, the restricted blood flow is usually sufficient. However, when you are active, the muscles do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients to function well and stay healthy.
Damage to peripheral arteries is usually caused by atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is the buildup of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on the artery walls. This accumulation is called plaque. The plaque can cause the arteries to narrow and block blood flow. The plaque can also rupture and lead to a blood clot.
Risk factors
Possible risk factors for peripheral arterial disease and claudication include:
- Atherosklerose, periphere arterielle Verschlusskrankheit oder Claudicatio in der Familienanamnese
- Alter über 50 Jahre, wenn Sie auch rauchen oder Diabetes haben
- Alter älter als 70 Jahre
- Chronisches Nierenleiden
- Diabetes
- Hoher Blutdruck
- Hoher Cholesterinspiegel
- Adipositas (ein Body-Mass-Index oder BMI über 30)
- Rauchen
Complications
Claudication is generally considered a warning of significant atherosclerosis, indicating an increased risk of heart attack or stroke. Other complications of peripheral artery disease due to atherosclerosis include:
- Hautläsionen, die nicht heilen
- Absterben von Muskel- und Hautgewebe (Gangrän)
- Amputation einer Gliedmaße
prevention
The best way to prevent claudication is to maintain a healthy lifestyle and control certain medical conditions. That means:
- Ernähren Sie sich gesund und ausgewogen
- Regelmäßig Sport treiben
- Wenn Sie Diabetes haben, halten Sie Ihren Blutzucker gut unter Kontrolle
- Ein gesundes Gewicht beibehalten
- Verwalten Sie Cholesterin und Blutdruck
- Hören Sie mit dem Rauchen auf, wenn Sie Raucher sind
Sources:
- Cameron AM, et al. Behandlung von Claudicatio. In: Aktuelle chirurgische Therapie. 13. Aufl. Elsevier; 2020. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Abgerufen am 6. Dezember 2019.
- Bonow RO, et al. Erkrankungen der peripheren Arterien. In: Herzkrankheit Braunwald: Ein Lehrbuch der Herz-Kreislauf-Medizin. 11. Aufl. Saunders Elsevier; 2019. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Abgerufen am 6. Dezember 2019.
- Neschis DG, et al. Klinische Merkmale und Diagnose der peripheren arteriellen Verschlusskrankheit der unteren Extremitäten. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Abgerufen am 30. Oktober 2021.
- Sidawy AN, et al. Arterielle Verschlusskrankheit der unteren Extremität: Medizinisches Management und Entscheidungsfindung. In: Rutherford’s Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy. 9. Aufl. Elsevier; 2019. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Abgerufen am 6. Dezember 2019.
- Atherosklerose. Merck Manual Professional-Version. https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/cardiovascular-disorders/arteriosclerosis/atherosclerose?query=atherosclerose. Abgerufen am 9. Dezember 2019.
- Harris L., et al. Epidemiologie, Risikofaktoren und Naturgeschichte der peripheren arteriellen Verschlusskrankheit der unteren Extremitäten. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Abgerufen am 30. Oktober 2021.
- Gerhard-Hermann MD, et al. 2016 AHA/ACC-Leitlinie zur Behandlung von Patienten mit peripherer arterieller Verschlusskrankheit der unteren Extremitäten: Ein Bericht der Task Force des American College of Cardiology/der American Heart Association zu Leitlinien für die klinische Praxis. Verkehr. 2017; doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000471.
- Harwood AE, et al. Übungstraining für Claudicatio intermittens: Eine narrative Überprüfung und Zusammenfassung von Richtlinien für Praktiker. BMJ Open Sport- und Bewegungsmedizin. 2020; doi:10.1136/bmjsem-2020-000897.
- Davis MG. Behandlung von Claudicatio aufgrund einer peripheren arteriellen Verschlusskrankheit. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Abgerufen am 30. Oktober 2021.
- Kithcart AP, et al. ACC/AHA versus ESC-Richtlinien für die Diagnose und Behandlung von peripherer arterieller Verschlusskrankheit. Zeitschrift des American College of Cardiology. 2018; doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.09.041.
- Afridi A. et al. Was sind die Auswirkungen verschiedener Arten des körperlichen Trainings bei Claudicatio intermittens – Eine Cochrane Review-Zusammenfassung mit Kommentar. Zeitschrift für Rehabilitationsmedizin. 2021; doi:10.2340/16501977-2820.

 Suche
Suche
 Mein Konto
Mein Konto