Inflammatory breast cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer
overview
Inflammatory breast cancer
Inflammatory breast cancer
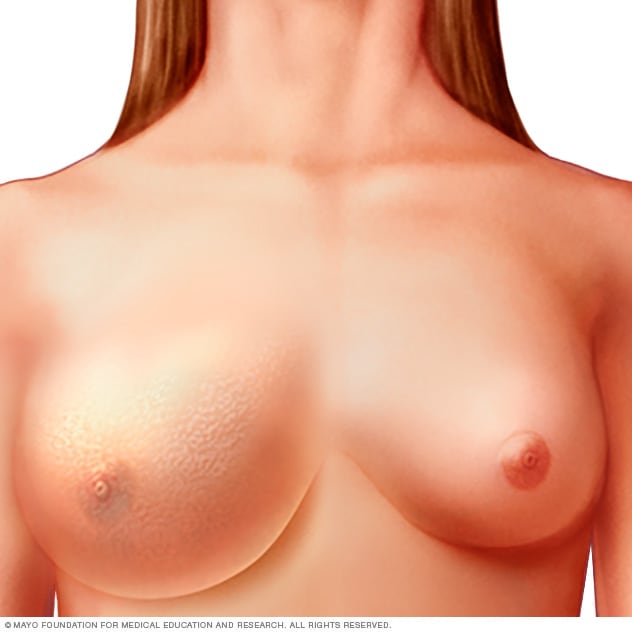
Inflammatory breast cancer often appears as an enlarged breast with red, thickened skin.
Inflammatory breast cancer is a rare form of breast cancer that develops quickly and makes the affected breast red, swollen, and tender.
Inflammatory breast cancer occurs when cancer cells block the lymphatic vessels in the skin that covers the breast, causing the breast's characteristic red, swollen appearance.
Inflammatory breast cancer is considered a locally advanced cancer - meaning it has spread from its site of origin to nearby tissue and possibly to nearby lymph nodes.
Inflammatory breast cancer can easily be confused with a breast infection, which is a much more common cause of breast redness and swelling. See a doctor immediately if you notice any skin changes on your breasts.
Symptoms
Inflammatory breast cancer usually does not form a lump like other forms of breast cancer do. Instead, signs and symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer include:
- Rasche Veränderung des Aussehens einer Brust über mehrere Wochen
- Dicke, Schwere oder sichtbare Vergrößerung einer Brust
- Verfärbung, die der Brust ein rotes, violettes, rosafarbenes oder gequetschtes Aussehen verleiht
- Ungewöhnliche Wärme der betroffenen Brust
- Grübchen oder Rillen auf der Haut der betroffenen Brust, ähnlich einer Orangenschale
- Zärtlichkeit, Schmerzen oder Schmerzen
- Vergrößerte Lymphknoten unter dem Arm, über dem Schlüsselbein oder unter dem Schlüsselbein
- Abflachung oder Einwärtsdrehung der Brustwarze
To diagnose inflammatory breast cancer, these symptoms must have been present for less than six months.
When to go to the doctor?
Make an appointment with your doctor if you notice any signs or symptoms that worry you.
Other more common diseases have signs and symptoms similar to inflammatory breast cancer. A breast injury or infection (mastitis) can cause redness, swelling, and pain.
Inflammatory breast cancer can easily be confused with a breast infection, which is much more common. It is reasonable and common to initially be treated with antibiotics for a week or longer. If your symptoms respond to antibiotics, no additional testing is necessary. However, if the redness does not improve, your doctor may consider more serious causes for your symptoms, such as: B. inflammatory breast cancer.
If you have been treated for a chest infection but your signs and symptoms persist, contact your doctor. Your doctor may recommend a mammogram or other test to evaluate your signs and symptoms. The only way to determine whether your symptoms are caused by inflammatory breast cancer is to have a biopsy to remove a sample of tissue for testing.
Causes
Anatomy of the breast
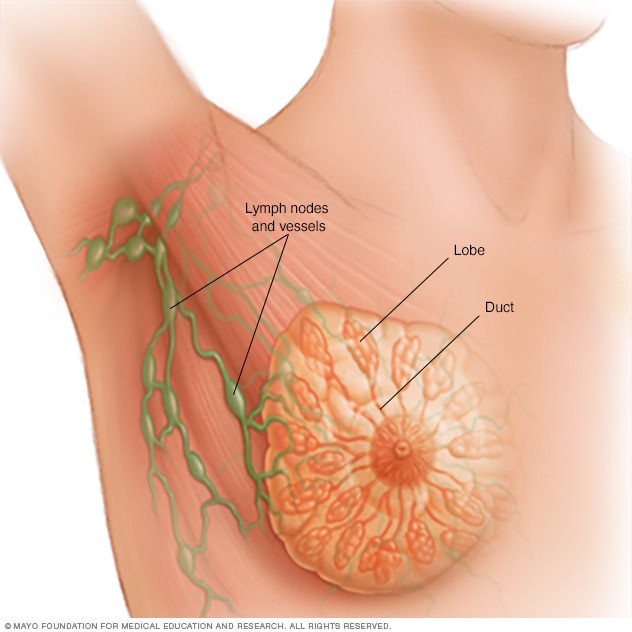
Anatomy of the breast
Each breast contains 15 to 20 lobes of glandular tissue arranged like the petals of a daisy. The lobes are further divided into smaller lobules that produce milk for breastfeeding. Small tubes (ducts) direct milk to a reservoir located just below your nipple.
It's not clear what causes inflammatory breast cancer.
Doctors know that inflammatory breast cancer begins when a breast cell develops changes in its DNA. Most often, the cell is located in one of the tubes (ducts) that transport breast milk to the nipple. The cancer can also originate in a cell in the glandular tissue (lobule) where breast milk is produced.
A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. The changes to the DNA tell the breast cell to grow and divide quickly. The accumulating abnormal cells infiltrate and block the lymphatic vessels in the skin of the breast. The blockage of the lymphatic vessels causes red, swollen, and dimpling skin - a classic sign of inflammatory breast cancer.
Risk factors
Factors that increase the risk of inflammatory breast cancer include:
- Frau sein. Frauen erkranken häufiger an entzündlichem Brustkrebs als Männer – aber auch Männer können an entzündlichem Brustkrebs erkranken.
- Jünger sein. Entzündlicher Brustkrebs wird häufiger bei Menschen zwischen 40 und 50 Jahren diagnostiziert.
- Schwarz sein. Schwarze Frauen haben ein höheres Risiko für entzündlichen Brustkrebs als weiße Frauen.
- Fettleibig sein. Übergewichtige Menschen haben im Vergleich zu Normalgewichtigen ein höheres Risiko für entzündlichen Brustkrebs.
Treatment of inflammatory breast cancer
Sources:
- Brustkrebs. Nationales umfassendes Krebsnetzwerk. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx. Abgerufen am 26. September 2019.
- Entzündlicher Brustkrebs. Nationales Krebs Institut. https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/ibc-fact-sheet. Abgerufen am 1. Oktober 2019.
- Menta A. et al. Entzündlicher Brustkrebs: Was Sie über diesen einzigartigen, aggressiven Brustkrebs wissen sollten. Chirurgische Kliniken von Nordamerika. 2018; doi:10.1016/j.suc.2018.03.009.
- Palliativpflege. Nationales umfassendes Krebsnetzwerk. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx. Abgerufen am 26. September 2019.
- Fragen Sie MayoExpert. Invasiver Brustkrebs (Erwachsener). Mayo-Klinik; 2019.
- Bland KI, et al., Hrsg. Entzündlicher Brustkrebs. In: Die Brust: Umfassendes Management gutartiger und bösartiger Erkrankungen. 5. Aufl. Elsevier; 2018. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Abgerufen am 27. September 2019.
- Mele M, et al. Entzündlicher Brustkrebs: Ein Rückblick aus unserer Erfahrung. Brustkrankheit. 2019; doi:10.3233/BD-1290365.

 Suche
Suche
 Mein Konto
Mein Konto