Ischemic colitis
Ischemic colitis
overview
Area commonly affected by ischemic colitis
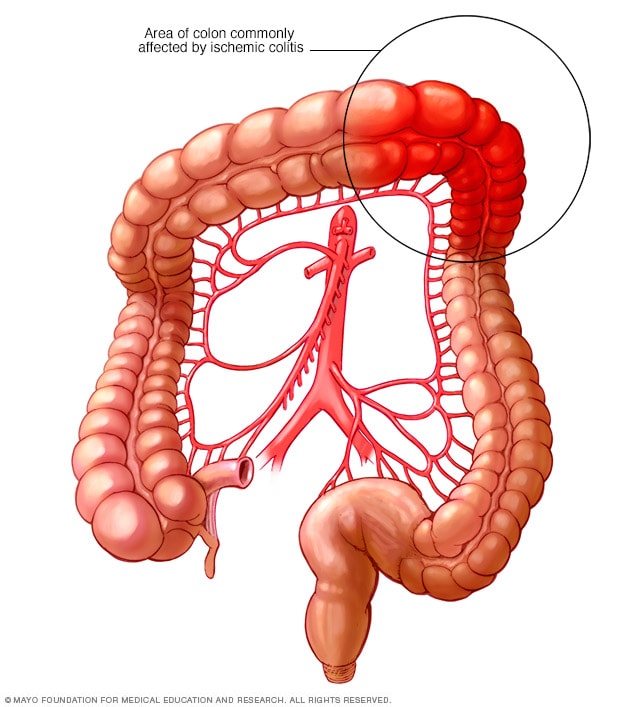
Area commonly affected by ischemic colitis
Ischemic colitis occurs when blood flow to part of the colon is reduced. The condition can affect any part of the colon, but is most common in the upper left segment.
Ischemic colitis occurs when blood flow to a part of the large intestine (colon) is temporarily reduced, usually due to a narrowing of the blood vessels that supply the colon or less blood flow through the vessels due to low pressure. The reduced blood flow does not provide enough oxygen to the cells in your digestive system, which can lead to tissue damage in the affected intestinal area.
Any part of the large intestine can be affected, but ischemic colitis most commonly causes pain in the left side of the abdominal area (abdomen).
Ischemic colitis can be misdiagnosed because it can easily be confused with other digestive problems. You may need medication to treat ischemic colitis or prevent infection, or you may need surgery if your colon has been damaged. However, ischemic colitis usually heals on its own.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of ischemic colitis may include:
- Schmerzen, Empfindlichkeit oder Krämpfe im Bauch, die plötzlich oder allmählich auftreten können
- Hellrotes oder kastanienbraunes Blut in Ihrem Stuhl oder manchmal nur Blutabgang ohne Stuhl
- Ein Gefühl der Dringlichkeit, Ihren Darm zu bewegen
- Durchfall
- Brechreiz
The risk of serious complications is higher if you have symptoms on the right side of your abdomen. This is less common compared to left-sided colitis. People with right-sided colitis tend to have more underlying medical problems, such as high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation and kidney disease. They require more surgery and also have a higher risk of mortality.
When to go to the doctor?
Seek immediate medical attention if you suddenly experience severe abdominal pain. Abdominal pain that makes you so uncomfortable that you can't sit still or find a comfortable position is a medical emergency.
Contact your doctor if you develop worrisome signs and symptoms such as bloody diarrhea. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent serious complications.
Causes
The exact cause of reduced blood flow to the colon is not always clear. But several factors can increase the risk of ischemic colitis:
- Ansammlung von Fettablagerungen an den Wänden einer Arterie (Arteriosklerose)
- Niedriger Blutdruck (Hypotonie) in Verbindung mit Dehydrierung, Herzinsuffizienz, Operation, Trauma oder Schock
- Darmverschluss durch einen Leistenbruch, Narbengewebe oder einen Tumor
- Chirurgie, die das Herz oder die Blutgefäße oder das Verdauungs- oder gynäkologische System betrifft
- Andere Erkrankungen, die Ihr Blut betreffen, wie z. B. Entzündung der Blutgefäße (Vaskulitis), Lupus oder Sichelzellenanämie
- Konsum von Kokain oder Methamphetamin
- Dickdarmkrebs (selten)
The role of medication
Use of certain medications can also lead to ischemic colitis, although this is rare. These medications include:
- Einige Herz- und Migränemedikamente
- Hormonmedikamente wie Östrogen
- Antibiotika
- Pseudoephedrin
- Opioide
- Bestimmte Medikamente für das Reizdarmsyndrom
- Chemotherapie-Medikamente
Risk factors
Risk factors for ischemic colitis include:
- Das Alter. Die Erkrankung tritt am häufigsten bei Erwachsenen über 60 Jahren auf. Ischämische Kolitis, die bei einem jungen Erwachsenen auftritt, kann ein Zeichen für eine Blutgerinnungsstörung oder eine Entzündung der Blutgefäße (Vaskulitis) sein.
- Sex. Ischämische Kolitis tritt häufiger bei Frauen auf.
- Gerinnungsstörungen. Erkrankungen, die die Blutgerinnung beeinflussen, wie z. B. Faktor-V-Leiden, können das Risiko einer ischämischen Kolitis erhöhen.
- Hoher Cholesterinspiegel, was zu Arteriosklerose führen kann.
- Reduzierte Durchblutung, aufgrund von Herzinsuffizienz, niedrigem Blutdruck, Schock oder bestimmten Erkrankungen wie Diabetes oder rheumatoider Arthritis.
- Vorherige Bauchoperation. Narbengewebe, das sich nach der Operation bildet, kann zu einer verminderten Durchblutung führen.
- Schwere Übung, wie Marathonläufe, die zu einer verminderten Durchblutung des Dickdarms führen können.
- Chirurgie unter Beteiligung der großen Arterie (Aorta), die Blut von Ihrem Herzen in den Rest Ihres Körpers pumpt.
Complications
Ischemic colitis usually improves on its own within two to three days. In more severe cases, the following complications may occur:
- Gewebetod (Gangrän) infolge verminderter Durchblutung
- Lochbildung (Perforation) in Ihrem Darm oder anhaltende Blutungen
- Darmverschluss (ischämische Striktur)
prevention
Because the cause of ischemic colitis is not always clear, there is no sure way to prevent the condition. Most people with ischemic colitis recover quickly and may never have another episode.
To prevent recurrent episodes of ischemic colitis, some doctors recommend eliminating any medications that might be causing the condition. Also be sure to stay hydrated, especially during vigorous outdoor activities - especially for those who live in warm climates. Testing for coagulation abnormalities may also be recommended, especially if no other cause of ischemic colitis is apparent.
Sources:
- Ferri FF. Ischämische Kolitis. In: Ferri’s Clinical Advisor 2021. Elsevier; 2021. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Abgerufen am 1. Oktober 2020.
- Cameron AM, et al. Management der ischämischen Kolitis. In: Aktuelle chirurgische Therapie. 13. Aufl. Elsevier; 2020. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Abgerufen am 1. Oktober 2020.
- Grubel P, et al. Dickdarmischämie. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Abgerufen am 1. Oktober 2020.
- Ischämische Kolitis. Merck Manual Professional-Version. https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/gastrointestinal-disorders/acute-abdomen-and-surgical-gastroenterology/ischämische-kolitis. Abgerufen am 1. Oktober 2020.
- Umar SB (Gutachten). Mayo-Klinik. 22. Oktober 2020.

 Suche
Suche
 Mein Konto
Mein Konto