Throat cancer
Throat cancer
overview
Parts of the throat (pharynx)
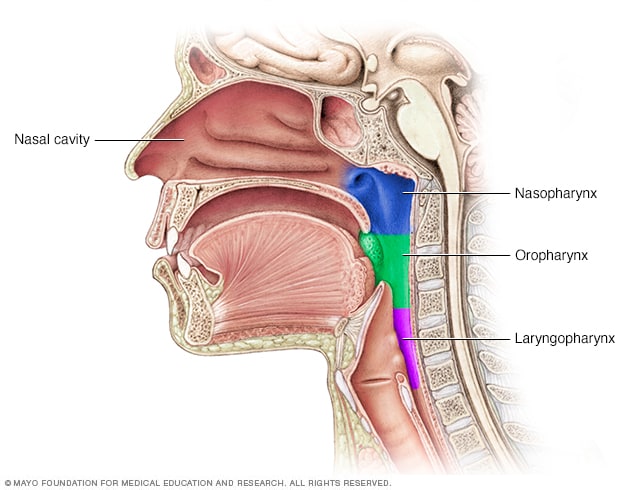
Parts of the throat (pharynx)
The throat (pharynx) is a muscular tube that runs from the bridge of the nose to the throat. It consists of three sections: nasopharynx, oropharynx and laryngopharynx, which is also called the hypopharynx.
Neck anatomy

Neck anatomy
The pharynx includes the esophagus, windpipe (trachea), larynx (larynx), tonsils, and epiglottis.
Throat cancer refers to cancer that develops in your throat (pharynx) or voice box (larynx).
Your throat is a muscular tube that starts behind your nose and ends at the back of your neck. Throat cancer most often begins in the flat cells that line the inside of your throat.
Your larynx sits just below your neck and is also susceptible to throat cancer. The larynx is made of cartilage and contains the vocal cords, which vibrate to produce sounds when speaking.
Types of throat cancer
Throat cancer is a general term for cancer that develops in the throat (pharyngeal cancer) or larynx (laryngeal cancer).
Although most throat cancers affect the same cell types, specific terms are used to differentiate the part of the throat where the cancer originates.
- Nasopharynxkrebs beginnt im Nasopharynx – dem Teil Ihres Rachens direkt hinter Ihrer Nase.
- Oropharynx-Krebs beginnt im Oropharynx – dem Teil Ihres Rachens direkt hinter Ihrem Mund, der Ihre Mandeln enthält.
- Hypopharynxkarzinom (Laryngopharynxkarzinom) beginnt im Hypopharynx (Laryngopharynx) – dem unteren Teil Ihres Rachens, direkt über Ihrer Speiseröhre und Luftröhre.
- Glottischer Krebs beginnt in den Stimmbändern.
- Supraglottischer Krebs beginnt im oberen Teil des Kehlkopfes und umfasst Krebs, der die Epiglottis betrifft, ein Knorpelstück, das verhindert, dass Nahrung in Ihre Luftröhre gelangt.
- Subglottischer Krebs beginnt im unteren Teil Ihres Kehlkopfes, unterhalb Ihrer Stimmbänder.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of throat cancer may include:
- Ein Husten
- Veränderungen in Ihrer Stimme, wie Heiserkeit oder undeutliches Sprechen
- Schluckbeschwerden
- Ohrenschmerzen
- Ein Knoten oder eine Wunde, die nicht heilt
- Halsschmerzen
- Gewichtsverlust
When to go to the doctor?
Make an appointment with your doctor if you notice new, persistent signs and symptoms. Most symptoms of throat cancer are not specific to cancer, so your doctor will likely investigate other, more common causes first.
Causes
Throat cancer occurs when cells in your throat develop genetic mutations. These mutations cause cells to grow uncontrollably and continue to live after healthy cells would normally die. The accumulating cells can form a tumor in your throat.
It is not clear what causes the mutation that causes throat cancer. However, doctors have identified factors that may increase your risk.
Risk factors
HPV and throat cancer

HPV and throat cancer
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a common sexually transmitted infection that increases the risk of certain types of throat cancer. HPV has been linked to cancer affecting the soft palate, tonsils, back of the tongue, and the side and back wall of the throat.
Factors that may increase your risk of throat cancer include:
- Tabakkonsum, einschließlich Rauchen und Kautabak
- Übermäßiger Alkoholkonsum
- Virusinfektionen, einschließlich humanem Papillomavirus (HPV) und Epstein-Barr-Virus
- Eine Ernährung ohne Obst und Gemüse
- Gastroösophageale Refluxkrankheit (GERD)
- Exposition gegenüber giftigen Stoffen bei der Arbeit
prevention
There is no proven way to prevent throat cancer from occurring. But to reduce your risk of throat cancer, you can:
- Hören Sie auf zu rauchen oder fangen Sie nicht an zu rauchen. Wenn Sie rauchen, hören Sie auf. Wenn Sie nicht rauchen, fangen Sie nicht an. Mit dem Rauchen aufzuhören kann sehr schwierig sein, also hole dir Hilfe. Ihr Arzt kann die Vorteile und Risiken der vielen Strategien zur Raucherentwöhnung wie Medikamente, Nikotinersatzprodukte und Beratung besprechen.
- Trinken Sie Alkohol nur in Maßen, wenn überhaupt. Wenn Sie sich entscheiden, Alkohol zu trinken, tun Sie dies in Maßen. Für gesunde Erwachsene bedeutet das bis zu einem Drink pro Tag für Frauen und bis zu zwei Drinks pro Tag für Männer.
- Wählen Sie eine gesunde Ernährung voller Obst und Gemüse. Die Vitamine und Antioxidantien in Obst und Gemüse können Ihr Risiko für Kehlkopfkrebs verringern. Essen Sie abwechslungsreiches buntes Obst und Gemüse.
- Schützen Sie sich vor HPV. Es wird angenommen, dass einige Rachenkrebsarten durch die sexuell übertragbare Infektion mit dem humanen Papillomavirus (HPV) verursacht werden. Sie können Ihr HPV-Risiko verringern, indem Sie die Anzahl Ihrer Sexualpartner einschränken und bei jedem Sex ein Kondom verwenden. Fragen Sie Ihren Arzt nach dem HPV-Impfstoff, der das Risiko von Kehlkopfkrebs und anderen HPV-bedingten Krebsarten verringern kann.
Treatment of throat cancer
Sources:
- Niederhuber JE, et al., Hrsg. Kopf-Hals-Krebs. In: Abeloffs Klinische Onkologie. 6. Aufl. Elsevier; 2020. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Abgerufen am 2. Oktober 2020.
- Flint PW, et al., Hrsg. Bösartige Tumore des Kehlkopfes. In: Cummings HNO-Heilkunde: Kopf- und Halschirurgie. 7. Aufl. Elsevier; 2021. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Abgerufen am 2. Oktober 2020.
- Kopf-Hals-Krebs. Nationales umfassendes Krebsnetzwerk. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx. Abgerufen am 2. Oktober 2020.
- Behandlung von Kehlkopfkrebs (Erwachsener) (PDQ) – Version für medizinisches Fachpersonal. Nationales Krebs Institut. https://www.cancer.gov/types/head-and-neck/hp/adult/laryngeal-treatment-pdq. Abgerufen am 17. November 2020.
- Behandlung von Hypopharynxkrebs (Erwachsener) (PDQ) – Version für medizinisches Fachpersonal. Nationales Krebs Institut. https://www.cancer.gov/types/head-and-neck/hp/adult/hypopharyngeal-treatment-pdq. Abgerufen am 17. November 2020.
- Fragen Sie MayoExpert. Oropharynxkarzinom, HPV-positiv, Stadium III bis IV: Beurteilung und Behandlung (Erwachsener). Mayo-Klinik; 2019.
- Sun L, et al. Die Nahrungsaufnahme von Flavonoiden reduziert das Risiko von Kopf- und Halskrebs, aber nicht von Speiseröhren- oder Magenkrebs bei Männern und Frauen in den USA. Das Journal für Ernährung. 2017; doi:10.3945/jn.117.251579.
- Matovia C, et al. Integrative Medizin bei Kopf-Hals-Tumoren. HNO-Heilkunde – Kopf- und Halschirurgie. 2017; doi:10.1177/0194599816671885.
- Warner KJ. Allscripts EPSi. Mayo-Klinik. 8. Juli 2020.
- Palliativpflege. Nationales umfassendes Krebsnetzwerk. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.aspx. Abgerufen am 2. Oktober 2020.
- Trinken neu denken: Alkohol und Ihre Gesundheit. Nationales Institut für Alkoholmissbrauch und Alkoholismus. https://www.rethinkingdrinking.niaaa.nih.gov/. Abgerufen am 17. November 2020.
- 2015-2020 Ernährungsrichtlinien für Amerikaner. US-Gesundheitsministerium und US-Landwirtschaftsministerium. https://health.gov/our-work/food-nutrition/2015-2020-dietary-guidelines/guidelines/. Abgerufen am 17. November 2020.
- Arten von Komplementärtherapien. Amerikanische Gesellschaft für klinische Onkologie. https://www.cancer.net/navigating-cancer-care/how-cancer-treatment/integrative-medicine/types-complementary-therapies. Abgerufen am 17. November 2020.

 Suche
Suche
 Mein Konto
Mein Konto