Meniere's disease
Meniere's disease
overview
Menière's disease is a disorder of the inner ear that can cause attacks of dizziness (vertigo) and hearing loss. In most cases, Menière's disease affects only one ear.
Menière's disease can occur at any age, but usually begins between young and middle adulthood. It is considered a chronic condition, but various treatments can help manage symptoms and minimize the long-term impact on your life.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of Meniere's disease include:
- Wiederkehrende Episoden von Schwindel. Sie haben ein Drehgefühl, das spontan beginnt und stoppt. Schwindelattacken treten ohne Vorwarnung auf und dauern in der Regel 20 Minuten bis mehrere Stunden, jedoch nicht länger als 24 Stunden. Starker Schwindel kann Übelkeit verursachen.
- Schwerhörigkeit. Hörverlust bei Morbus Meniere kann kommen und gehen, besonders früh. Schließlich haben die meisten Menschen einen dauerhaften Hörverlust.
- Klingeln im Ohr (Tinnitus). Tinnitus ist die Wahrnehmung eines klingelnden, summenden, brüllenden, pfeifenden oder zischenden Geräusches in Ihrem Ohr.
- Völlegefühl im Ohr. Menschen mit Morbus Menière verspüren häufig Druck in einem betroffenen Ohr (Gehördruck).
After an episode, signs and symptoms improve and may disappear for a while. Over time, the frequency of episodes may decrease.
When to go to the doctor?
See your doctor if you have any signs or symptoms of Meniere's disease. These problems can be caused by other illnesses and it is important to get an accurate diagnosis as quickly as possible.
Causes
Inner ear and balance
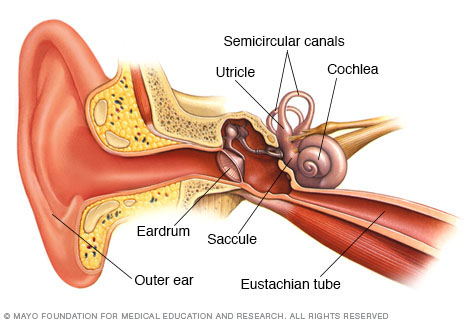
Inner ear and balance
Semicircular canals and otolith organs—utricle and saccule—in your inner ear contain fluid and fine, hair-like sensors that help you focus your eyes on a target when your head moves and help you maintain your balance.
The cause of Menière's disease is unknown. The symptoms of Menière's disease appear to be the result of an abnormal amount of fluid (endolymph) in the inner ear, but it is not clear what causes this.
Factors affecting fluid that could contribute to Meniere's disease include:
- Unsachgemäßer Flüssigkeitsabfluss, möglicherweise aufgrund einer Blockade oder anatomischen Anomalie
- Abnorme Immunantwort
- Virusinfektion
- Genetische Veranlagung
Because no single cause has been identified, it is likely that Meniere's disease is due to a combination of factors.
Complications
The unpredictable attacks of dizziness and the prospect of permanent hearing loss can be the most difficult problems of Meniere's disease. The disease can unexpectedly interrupt your life and cause fatigue and stress.
Dizziness can cause you to lose balance and increase your risk of falls and accidents.
Sources:
- Ferri FF. Morbus Menière. In: Ferri’s Clinical Advisor 2019. Philadelphia, Pa.: Elsevier; 2019. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Abgerufen am 1. November 2018.
- Dinces EA, et al. Menière-Krankheit. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Abgerufen am 1. November 2018.
- Morbus Menière. American Academy of Otolaryngology – Kopf- und Halschirurgie. https://www.enthealth.org/conditions/menieres-disease/. Abgerufen am 2. November 2018.
- Morbus Menière. Verband für Vestibularisstörungen. http://vestibular.org/menieres-disease. Abgerufen am 1. November 2018.
- Morbus Menière. Nationales Institut für Taubheit und andere Kommunikationsstörungen. https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/menieres-disease. Abgerufen am 1. November 2018.
- Diagnose. Verband für Vestibularisstörungen. https://vestibular.org/understanding-vestibular-disorder/diagnosis. Abgerufen am 1. November 2018.
- Van Sonsbeek S, et al. Überdrucktherapie bei Ménière-Krankheit oder -Syndrom (Review). Cochrane-Datenbank systematischer Reviews. http://www.thecochranelibrary.com. Abgerufen am 1. November 2018.
- Wie viel Natrium sollte ich pro Tag essen? American Heart Association. https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/sodium/how-much-sodium-should-i-eat-per-day. Abgerufen am 1. November 2018.
- Lopez-Escamez JA, et al. Diagnostische Kriterien für Morbus Menière. Journal of Vestibular Research: Gleichgewicht & Orientierung. 2015;25:1.

 Suche
Suche
 Mein Konto
Mein Konto