4 Types of Thyroid Diseases
The thyroid gland, located just below the Adam's apple in the neck, is a butterfly-shaped gland that is a prestigious part of the complex network of glands called the endocrine system. While the endocrine system is responsible for synchronizing the activities of multiple bodies, the thyroid's sole function is to release thyroid hormone. Thyroid hormones regulate the entire metabolism of the body, and therefore a disruption in the body can cause numerous serious diseases. If you want to know the most common disorders caused by thyroid dysfunction, this article is definitely for you. Hashimoto's disease Commonly known as hypothyroidism, it is a chronic...
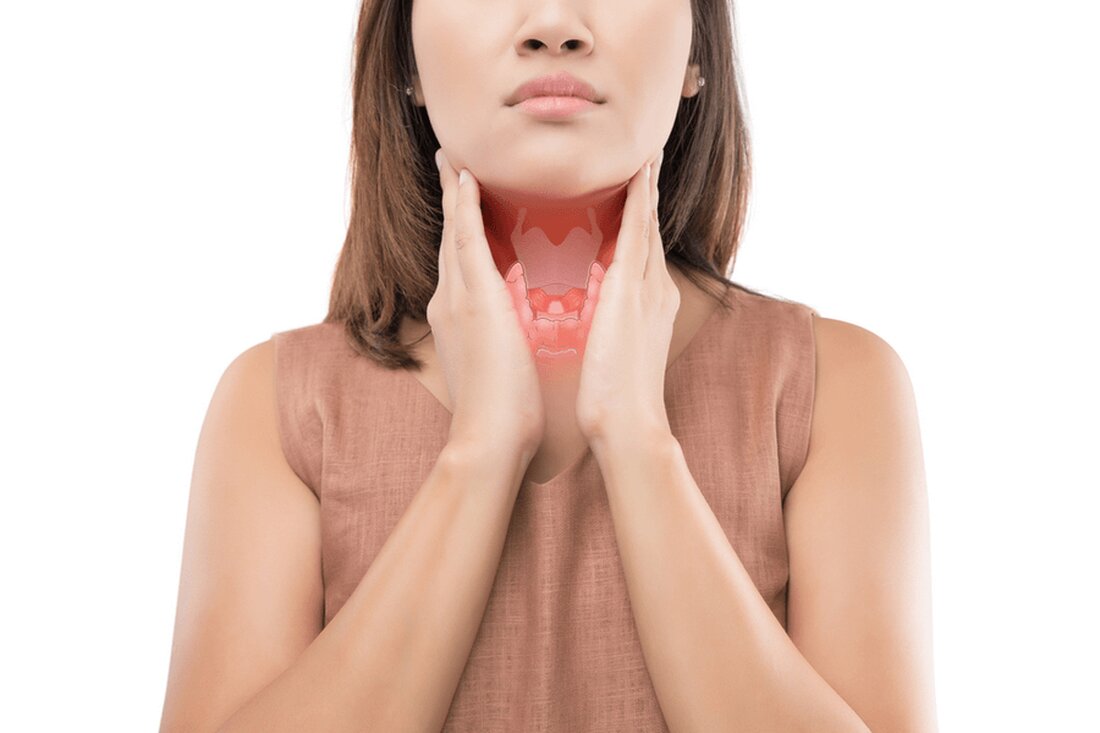
4 Types of Thyroid Diseases
The thyroid gland, located just below the Adam's apple in the neck, is a butterfly-shaped gland that is a prestigious part of the complex network of glands called the endocrine system. While the endocrine system is responsible for synchronizing the activities of multiple bodies, the thyroid's sole function is to release thyroid hormone. Thyroid hormones regulate the entire metabolism of the body, and therefore a disruption in the body can cause numerous serious diseases.
If you want to know the most common disorders caused by thyroid dysfunction, this article is definitely for you.
Hashimoto's disease
Commonly known as hypothyroidism, it is a chronic disease that can occur at any age. The disease begins when the body's immune system destroys the thyroid gland, completely manipulating its ability to release thyroid hormone. People with mild hypothyroidism may not show any obvious symptoms, but people with severe temperament may show symptoms such as:
-
constipation
-
Dry skin, thin hair
-
depression
-
Fatigue
-
Swollen, pale face
-
Weight gain
-
Cold intolerance
-
Unbalanced measurement cycle (for women)
-
Enlarged thyroid (goiter)
Graves' disease
Named after the doctor who first revealed it, it is a common form of overactive thyroid, or hyperthyroidism. It is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body's immune system attacks the thyroid gland and therefore leads to overproduction of thyroid hormone. With high levels of thyroid in the blood, the body may show symptoms such as:
-
Menstrual irregularities
-
Muscle weakness
-
Heat intolerance
-
Profuse sweating
-
Fatigue
-
Bulging eyes and incorrect vision
-
Frequent bowl movements or even diarrhea
-
Hand tremor
-
Cardiac arrhythmia
goiter
A non-cancerous result of thethyroidGland, goiter is widespread worldwide and is mainly considered to be a result of a lack of iodine in the body. Goiter can occur at any age, but is common in people over 40. Medical history, pregnancy, radiation exposure and use of certain medications are the main risk factors for this disease. Mild cases of goiter may not show any symptoms, while complex cases of goiter may present with the following symptoms:
-
Tightness/swelling in the neck
-
Wheezing or coughing
-
Hoarseness of voice
-
Difficulty breathing and/or swallowing food
Thyroid nodules
Thyroid disease can also lead to another acute condition known as thyroid nodules. The nodules are the growths in or on the thyroid gland. However, the main cause of this disease is not known, but it is observed that it may be cancerous in a small proportion of cases. The risks associated with thyroid nodules may increase with age. Thyroid nodules do not show any symptoms, but if they become large enough they can lead to symptoms such as:
-
Tremble
-
Damp skin
-
Increased appetite
-
High pulse rate
-
nervousness
-
weight loss
-
Swelling in the neck
-
Problem swallowing and breathing
-
High pain
Every thyroid condition is different, and therefore treatment options differ for each. To ensure you don't experience any major side effects, it's important to see a specialist, get a proper diagnosis, and adhere to treatment.
Inspired by Poulami Deb

 Suche
Suche
 Mein Konto
Mein Konto
